New Energy & Power
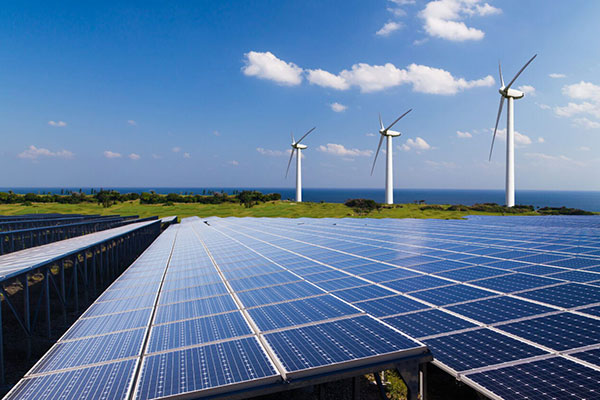
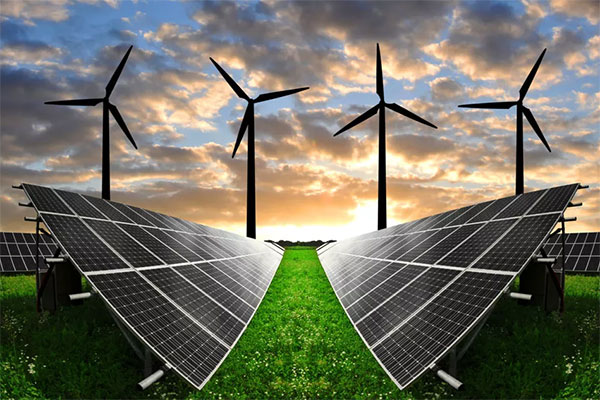



Clean and renewable energy has been the mainstream trend of global development. Solar and wind power generation systems produce huge amounts of electricity by inverter conversion and feed the power grid, and a large number of control chip sets manage the operation of multiple energy collection plants.owns a complete advanced supply chain. By using efficient and economic material such as extrusion aluminum, die casting aluminum, plus precision CNC machining, durable surface coating protection technology, Ruiqifeng can provide high power heat sinks to protecting their inverters and control chip sets. Thus they can operate stably and efficiently with minimum power loss and longest long life cycle.
Automobile Industry
Due to its light weight,aluminum is more suitable for manufacturing automobiles than other metals.We can provide a variety of lightweight and wear-resistant automotive aluminum to ensure safety of these products in automobiles.


Building Contruction
Aluminum windows and doors are made of aluminum building profiles.and its window structure is divided into ordinary aluminum alloy doors and windows and thermally insulated aluminum alloy doors and windows.Aluminum windows have the characteristics of beauty. sealing and high strength. It is widely used in the construction. In home decoration,aluminum doors and windows are usually used for balconies
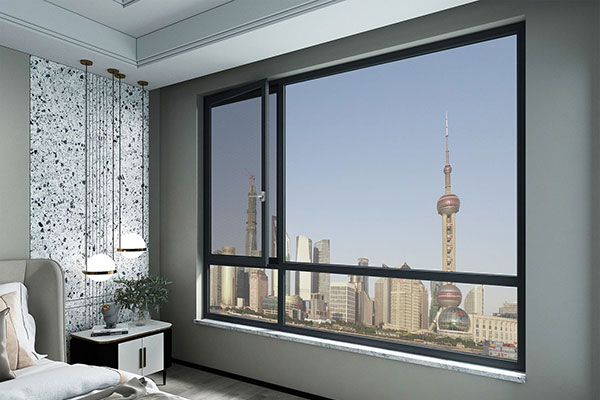
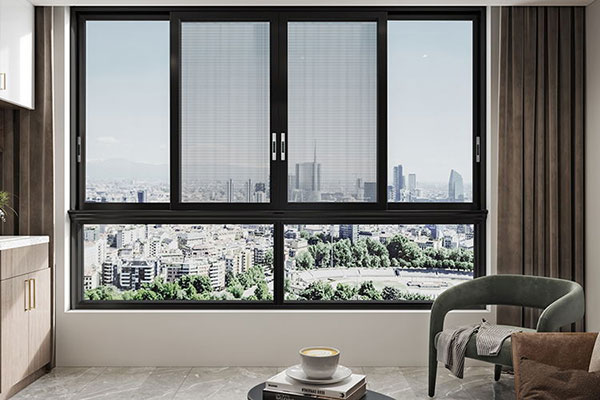
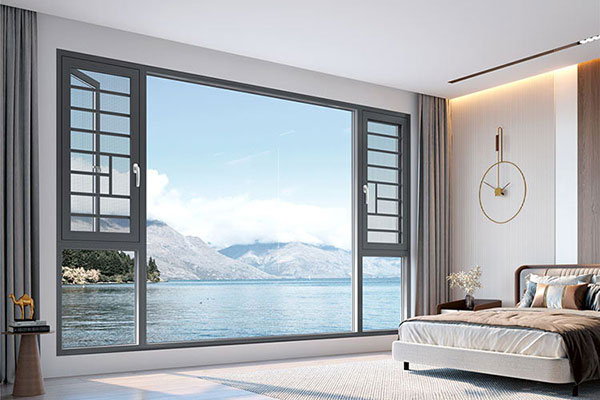
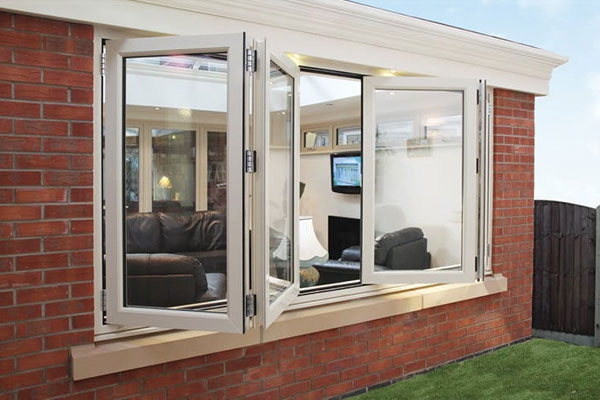






Wireless Communication
Aluminum heat sink is an important heat dissipation component widely used in wireless communication technology. In wireless communication equipment, components such as wireless signal processors, power amplifiers, and radio frequency modules will generate a large amount of heat. If the heat cannot be dissipated in time, it will cause the equipment to overheat and affect the performance and life of the equipment. Therefore, aluminum heat sinks play a vital role in wireless communication equipment.
First of all, aluminum radiators have good thermal conductivity properties. Aluminum has a high thermal conductivity and can quickly conduct heat from the heating element to the surface of the radiator, and effectively radiate heat to the surrounding environment through the surface area of the radiator. This allows the aluminum heat sink to quickly remove heat from the wireless communications device, preventing the device from overheating.Secondly, aluminum radiators have good heat dissipation design and structure. Aluminum radiators usually use multiple structures such as heat sinks and fins to increase the heat dissipation area, and use fans or air ducts to enhance the heat dissipation effect. This design can not only increase the heat dissipation area, but also improve air circulation and promote effective heat dissipation. In addition, aluminum heat sinks are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making them ideal for the requirements of wireless communication equipment. Due to the low density of aluminum, the aluminum heat sink is not only lightweight, but can also meet the compact and lightweight requirements of wireless communication equipment. At the same time, the surface of aluminum radiators is usually oxidized or anodized, which increases its anti-corrosion performance and can be used for a long time in harsh working environments. Finally, aluminum radiators are relatively low-cost to make and suitable for mass production. Aluminum is a common metal material with low purchasing and processing costs. Compared with other high-performance heat dissipation materials, aluminum heat sinks can find a good balance between performance and cost, providing cost-effective heat dissipation solutions for wireless communication equipment.
In summary, aluminum heat sinks have a wide range of applications in the field of wireless communications. They dissipate heat quickly and efficiently to maintain the normal operating temperature of the device, while being lightweight, corrosion-resistant and low-cost. In wireless communication equipment, aluminum heat sinks are an indispensable part and make important contributions to the stable performance and extended life of the equipment.
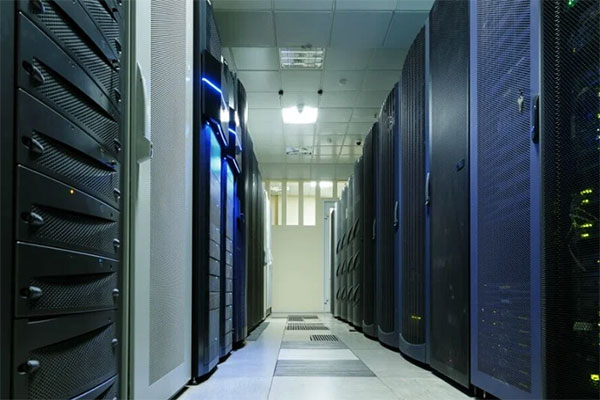



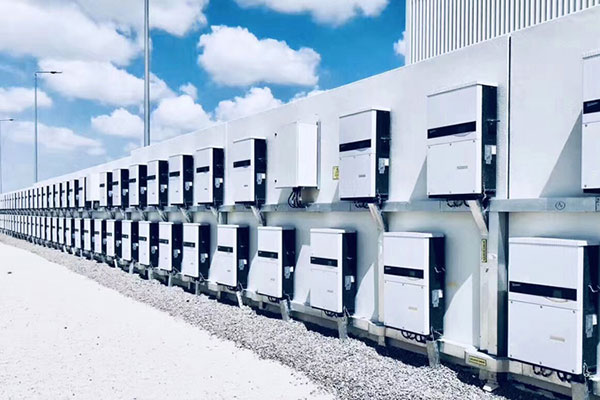
Electric Power & Power Supply
UPS, or uninterruptible power supply, is a crucial system equipment that bridges the gap between the battery and the main engine of a device or system. Its primary function is to convert direct current (DC) into mains power through the use of module circuits, such as the main engine inverter. UPS systems are mainly utilized in various applications, including single computers, computer network systems, and other power electronic equipment like solenoid valves and pressure transmitters, to provide a stable and uninterrupted power supply. The significance of UPS power supply in modern-day operations cannot be understated.With the ever-increasing reliance on technology, power outages and fluctuations can bring significant challenges, disrupt operations, and potentially damage sensitive equipment. The role of a UPS system is to ensure continuity by providing backup power during such events. This functionality not only safeguards critical systems but also contributes to increased productivity, data integrity, and protection against financial losses. In order for a UPS system to perform optimally, the prevention of overheating is of utmost importance.
Heat is generated due to the conversion process and constant operation of electrical components within the system. If not efficiently managed, this heat can lead to malfunctions, component failures, and overall degradation of the equipment's performance. This is where the role of an aluminum extruded heat sink comes into play. Aluminum extruded heat sinks are widely used in UPS systems to facilitate effective heat dissipation. The extrusion process creates a high surface area-to-volume ratio, allowing for efficient transfer of heat from the UPS system to the surrounding environment. These heat sinks are typically attached to components that generate the most heat, such as power transistors or other high-power devices. By doing so, the heat sinks act as thermal conductors, absorbing the excess heat and dispersing it into the surrounding air. The design and size of the aluminum extruded heat sink play a crucial role in optimizing heat dissipation. Factors such as the fins' width, height, and spacing, as well as the overall surface area, must be carefully considered to ensure efficient cooling. Additionally, the use of cooling fans or natural convection can further enhance the heat dissipation process, particularly in applications where the ambient temperature is high or the system operates under heavy load conditions. By incorporating aluminum extruded heat sinks into UPS systems, manufacturers ensure the normal operation and longevity of the equipment. These heat sinks aid in reducing operating temperatures, preventing overheating-related issues, and preserving the integrity and reliability of the UPS system. The effective dissipation of heat helps to maintain the internal components within their safe operating temperatures, thereby extending their lifespan and enhancing overall system performance.
In conclusion, UPS systems play a vital role in providing continuous and stable power supply in various applications. The efficient dissipation of heat is crucial to ensuring the normal operation and longevity of the equipment. Aluminum extruded heat sinks serve as a key component in managing heat generated by UPS systems, allowing for optimal performance and protection against potential damage caused by overheating. Thus, their importance cannot be overlooked in the design and implementation of UPS power supply solutions.
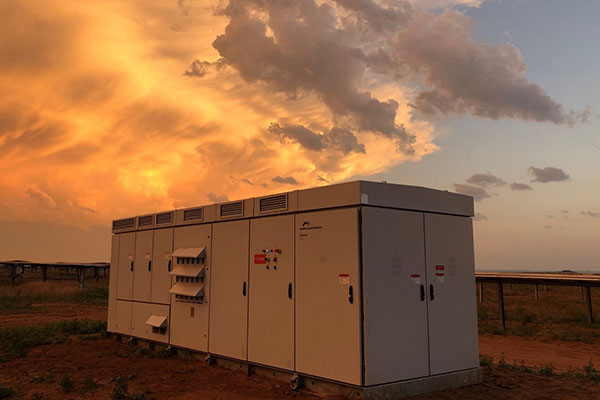
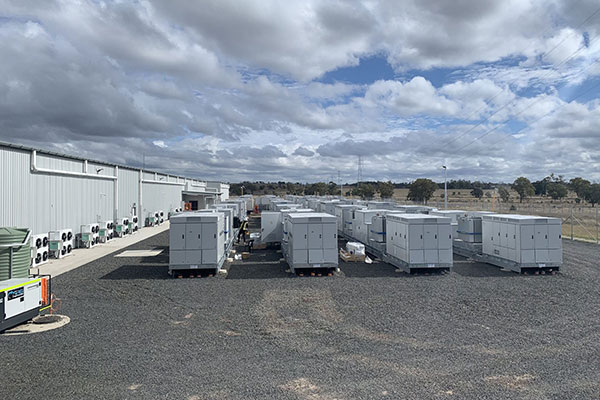
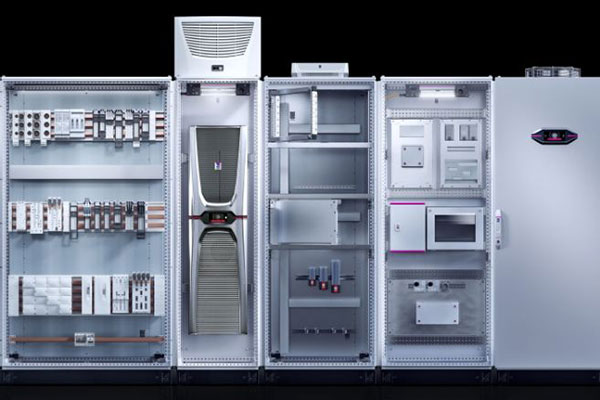



Consumer Electronic
A heat sink plays a crucial role in managing the heat generated by electronic or mechanical devices, ensuring that they operate within their safe temperature limits. It is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat from the device to a fluid medium, such as air or liquid coolant, where it can be dissipated effectively.
In the context of computers, heat sinks are commonly used to cool central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), chipsets, and RAM modules. These components tend to generate a significant amount of heat during operation, and without proper cooling, they can quickly overheat, leading to performance degradation or even component failure. The design and construction of a heat sink are critical for efficient heat dissipation. Most heat sinks utilize a finned structure made of a thermally conductive material like aluminum or copper. The fins increase the surface area of the heat sink, allowing for greater contact with the surrounding fluid medium and enhancing heat transfer. When an electronic device operates, heat is generated at the component level, such as the CPU or GPU. The heat is conducted through the device's body, and to prevent overheating, it needs to be dissipated to the surrounding environment. This is where the heat sink comes into play. The heat sink is attached to the hot component, which serves as a thermal pathway for the heat to flow from the component to the heat sink. Once the heat is transferred to the heat sink, it needs to be dissipated effectively to maintain the device's temperature within safe limits. Air cooling is the most common method, where the heat sink is exposed to the surrounding air. The large surface area of the heat sink fins allows for efficient heat dissipation through convection. The surrounding air absorbs the heat and carries it away, cooling down the heat sink and the attached component. In more demanding applications or when dealing with extremely high heat loads, liquid cooling can be used. Liquid coolant circulates through a heat sink, absorbing the heat, and then carries it to a radiator where it can be dissipated. Liquid cooling offers higher thermal conductivity than air cooling, allowing for enhanced heat dissipation and potentially lower operating temperatures. Heat sinks are not limited to computers; they are also extensively used in high-power semiconductor devices such as power transistors, lasers, and LEDs. These devices generate significant heat during operation, and without effective heat management, their performance and reliability can be compromised. Heat sinks in these applications are typically custom-designed to meet the specific thermal requirements of the device.
In conclusion, heat sinks are essential components in electronic and mechanical systems, regulating the temperature of devices by efficiently transferring and dissipating heat. Whether in computers, power transistors, or optoelectronics, heat sinks play a critical role in maintaining device performance, preventing overheating, and ensuring the longevity and reliability of the components.