Why Choose Aluminium Heat Sink Material for Efficient Thermal Management?
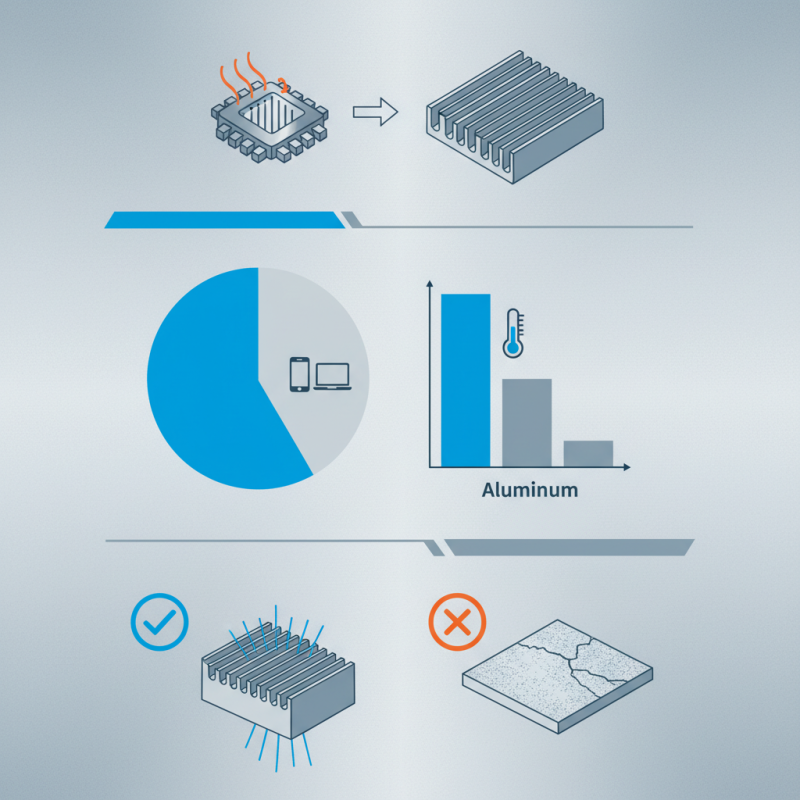
In the quest for efficient thermal management, one material stands out: Aluminium Heat Sink Material. This metal is widely recognized for its excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight properties. According to a 2021 report by the International Aluminium Institute, aluminium has a thermal conductivity of around 205 W/m·K. This makes it an ideal candidate for heat dissipation in electronics.
Many industries rely on aluminium heat sinks for cooling applications. Data from the Semiconductor Industry Association indicates that around 60% of modern consumer electronics utilize aluminium heat sinks. This growing trend emphasizes the importance of this material in maintaining optimal performance. However, there are challenges, such as surface oxidation, which can affect thermal efficiency.
Choosing Aluminium Heat Sink Material is often a practical decision, but not without its pitfalls. Some companies overlook the need for proper surface finishing. This can lead to reduced thermal performance. Understanding both the benefits and potential drawbacks of aluminium is crucial for engineers. Such an awareness fosters better design and implementation in thermal management systems.
Understanding the Importance of Thermal Management in Electronics
Thermal management plays a critical role in electronics. As devices become smaller and more powerful, managing heat becomes essential. Poor thermal management can lead to device failure or reduced performance. According to industry reports, up to 50% of electronic component failures are linked to overheating.
Aluminium is a popular choice for heat sinks due to its excellent thermal conductivity. It dissipates heat efficiently, maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Studies show that aluminium heat sinks can reduce junction temperatures by more than 20% compared to other materials. This can significantly extend the lifespan of electronic components. Still, we must acknowledge that relying solely on a single material is not always effective.
Designing an efficient thermal management system requires careful consideration. Factors such as airflow, ambient temperatures, and insulation can also influence effectiveness. Sometimes, engineers overlook these details. Inadequate ventilation can negate the benefits of an aluminium heat sink. Balancing all elements in thermal management is essential for achieving peak performance.
Thermal Conductivity of Common Heat Sink Materials
Overview of Aluminium as a Heat Sink Material

Aluminium has become a popular choice for heat sink materials due to its numerous advantages. This lightweight metal is known for its excellent thermal conductivity, which helps in efficient heat dissipation. In applications ranging from electronics to automotive, managing heat is crucial for device performance. Aluminium ensures that heat is drawn away rapidly, preventing overheating.
The construction of aluminium heat sinks provides unique design opportunities. These heat sinks can be extruded into various shapes, maximizing surface area. More surface area means enhanced thermal management. Aluminium is also easy to work with, allowing for customized solutions. However, this flexibility requires careful thought in design. If not optimized, the heat sink may still fall short of expected performance.
Another important factor is the durability of aluminium. It resists corrosion, which prolongs its lifespan in various environments. But, if not properly coated, it can still face issues. The trade-off between weight and strength needs careful examination. While aluminium is lighter, it might not be suitable for all high-stress applications. These considerations highlight the need for a balanced approach when selecting materials.
Key Advantages of Aluminium Over Other Materials for Heat Sinks
Aluminium has emerged as a top choice for heat sink materials, thanks to its unique properties. Its thermal conductivity averages around 205 W/mK, significantly surpassing many other metals. This high level of conductivity enables faster heat dissipation, ultimately improving device efficiency. Additionally, aluminium's lightweight nature makes it ideal for applications where weight is a concern. Reports indicate that weight reductions of up to 50% are achievable by using aluminium instead of copper, a commonly used alternative.
Another key advantage is aluminium's resistance to corrosion. It forms a protective oxide layer, which enhances its longevity. For outdoor applications or humid environments, this durability cannot be overlooked. Data shows that aluminium heat sinks can last substantially longer than those made from other materials, resulting in lower replacement costs over time. Many engineers also appreciate the ease of fabrication. Aluminium can be easily extruded or machined to create complex shapes, catering to specific cooling requirements. Yet, this versatility means that manufacturers must remain attentive to the balance of cost and performance.
While the advantages are clear, it's essential to be aware of some limitations. The thermal performance of an aluminium heat sink can be influenced by design parameters, such as surface area and airflow. If not optimized, this could lead to underwhelming results in thermal management. Engineers are often challenged to find the right balance between design complexity and thermal efficiency, highlighting the need for ongoing innovation in this space.
Why Choose Aluminium Heat Sink Material for Efficient Thermal Management? - Key Advantages of Aluminium Over Other Materials for Heat Sinks
| Feature | Aluminium | Copper | Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 205 | 400 | 50 |
| Weight (g/m³) | 2700 | 8960 | 7850 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate | Poor |
| Manufacturing Cost | Low | High | Moderate |
| Ease of Fabrication | High | Medium | Low |
| Recyclability | 100% | 90% | 50% |
Applications of Aluminium Heat Sinks in Various Industries
Aluminium heat sinks are widely used across various industries for effective thermal management. Their lightweight nature makes them ideal for applications where weight is a concern. For example, in the automotive sector, these heat sinks help dissipate heat from critical engine components. This improves overall performance and prevents overheating.
In the electronics industry, aluminium heat sinks are essential. They are used in devices like CPUs and power amplifiers. By efficiently managing heat, these components can function better and last longer. Even in renewable energy, aluminium heat sinks play a vital role. They are key in solar inverters and LED lighting systems, contributing to the overall efficiency of these technologies.
Despite their advantages, not every aluminium heat sink design optimizes thermal performance. Some structures might not maximize airflow, reducing their effectiveness. Companies often need to reconsider their designs to improve heat dissipation. Balancing cost and performance is challenging, and sometimes, a trade-off occurs. Understanding these nuances can lead to better products in the long run.
Best Practices for Designing Efficient Aluminium Heat Sink Solutions

Aluminium heat sinks are popular for their efficient thermal management capabilities. When designing these solutions, it’s essential to consider the material properties. Aluminium has excellent thermal conductivity, allowing heat to dissipate quickly. Its lightweight nature makes installation easier. Architects and engineers often overlook the importance of selecting the right thickness and surface area, which can lead to inefficiencies.
Creating an effective heat sink involves precise calculations. One must analyze the heat source's output. Ignoring airflow and orientation can produce unexpected thermal hotspots. Using simulation tools can help visualize airflow patterns. Engineers sometimes focus too much on aesthetics rather than functionality. Streamlined designs might look good but could hinder cooling performance.
While aluminium is effective, it faces challenges like oxidation. Coatings and surface treatments can mitigate these issues. However, they can add complexity to the design process. Regular testing is vital to ensure the heat sink performs optimally. It's important to revisit designs after real-world trials. Continuous improvement is key to achieving the best results in thermal management. Each design iteration should aim for efficiency while overcoming previous shortcomings.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Best Aluminium Profile for Doors and Windows Installation
-

2026 How to Optimize the Aluminium Process for Maximum Efficiency?
-

2026 Top Aluminium Profile For Doors And Windows Trends to Watch?
-
2026 Top Trends in Aluminium T Slot Profile Systems What You Need to Know?
-

Top 10 Aluminium Door China Options for Your Home?
-
Top 10 Benefits of Choosing Aluminium Windows in Turkey for Your Home