Top 10 Aluminium Extrusion Heat Sink Designs for Optimal Cooling Solutions?
In the fast-evolving world of electronic cooling, the importance of effective thermal management cannot be overstated. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned expert in thermal engineering, "Aluminium Extrusion Heat Sinks are vital for maintaining optimal temperatures in high-performance devices." Her insight highlights the necessity of innovative designs that enhance cooling efficiency.
Aluminium Extrusion Heat Sinks offer unique advantages. They are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and capable of dissipating heat effectively. Engineers often face challenges when designing these heat sinks. The need for improved performance and cost-effectiveness can conflict. Furthermore, the design process requires a balance between thermal performance and aesthetic appeal.
Many designs excel in cooling solutions yet may overlook certain aspects. For example, some heat sinks might be more efficient but less practical for everyday use. Engineers must reflect on these trade-offs. Continuous innovation in Aluminium Extrusion Heat Sink designs is essential to meet the growing demands of modern technology. There is always room for improvement. How can we optimize these designs further? This question remains crucial as we explore the top ten Aluminium Extrusion Heat Sink designs that promise better cooling solutions.

Overview of Aluminium Extrusion Heat Sink Technology
Aluminium extrusion heat sinks are key components in modern cooling technology. They are designed to dissipate heat effectively, improving the performance of electronic devices. The extrusion process allows for complex shapes and sizes, which can maximize surface area and enhance cooling efficiency. This is crucial in high-performance applications, such as in computer processors and LED lights.
One notable aspect of these heat sinks is their lightweight nature combined with robust thermal conductivity. This makes them ideal for various applications. However, achieving the perfect design is often a challenge. Factors like airflow, ambient temperature, and power density all play a significant role in a heat sink's effectiveness. Designers often find themselves refining their prototypes multiple times to address thermal hotspots or inefficient airflow patterns.
The versatility of aluminium extrusion offers an array of design possibilities, but not all designs meet performance expectations. Some may focus too much on aesthetics, neglecting thermal efficiency. Others could be too bulky for compact devices. It's essential to strike a balance between form, function, and manufacturing feasibility. Continuous improvement in design processes can lead to better cooling solutions, but it often requires iterative testing and critical analysis.
Key Design Principles for Effective Heat Dissipation
When considering aluminium extrusion heat sink designs, effective heat dissipation hinges on key principles. The surface area plays a vital role. The more area available, the better the heat can disperse. Studies indicate that increasing the surface area by just 20% can improve cooling efficiency significantly. Fins and grooves are common features that enhance this effect. These designs facilitate airflow, enabling cooler temperatures.
Material choice is also critical. Aluminium has excellent thermal conductivity, making it a preferred option in many applications. Reports highlight that aluminium can conduct heat up to 235 W/m·K. However, not all extrusions are created equal. Some may have defects or inconsistent thickness. These imperfections affect performance.
**Tip:** Regularly inspect the heat sink for physical damage. Small dents or scratches can disrupt airflow and thermal conductivity.
Designing for airflow is essential. Proper orientation can influence how well air moves around the fins. Tests show that angled fins can offer a 30% increase in airflow compared to vertical ones.
**Tip:** Experiment with different angles in prototypes. Don't hesitate to iterate on the design as small adjustments can yield significant improvements.
Top 10 Aluminium Extrusion Heat Sink Designs for Optimal Cooling Solutions
| Design Name | Dimensions (mm) | Surface Area (cm²) | Weight (g) | Cooling Efficiency (W/K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Plate | 100 x 100 x 10 | 400.00 | 150 | 10 |
| Vertical Fins | 120 x 80 x 20 | 480.00 | 200 | 12 |
| Horizontal Fins | 150 x 100 x 15 | 440.00 | 180 | 11 |
| Pin Fin | 90 x 90 x 25 | 500.00 | 220 | 15 |
| Dome Shape | 110 x 110 x 30 | 550.00 | 250 | 16 |
| Cross Section | 130 x 60 x 18 | 460.00 | 190 | 13 |
| Wavy Surface | 140 x 80 x 22 | 520.00 | 230 | 14 |
| Hexagonal Design | 100 x 100 x 35 | 600.00 | 300 | 17 |
| Circular Fins | 120 x 120 x 30 | 520.00 | 240 | 15 |
| L-Shaped | 100 x 100 x 20 | 450.00 | 170 | 12 |
Top 10 Innovative Aluminium Extrusion Heat Sink Designs
Aluminum extrusion heat sinks are vital for effective thermal management in electronics. Recent studies indicate that efficient cooling can enhance performance by up to 30%. Innovative designs can significantly improve thermal dissipation while minimizing size. This balance is crucial in compact devices where space is limited.
One promising design features fin structures that maximize surface area. These fins can vary in thickness and spacing, impacting airflow and cooling. Another design incorporates a dual-channel approach. This allows for concurrent airflow, increasing heat transfer rates. Engineers emphasize the importance of materials; the right alloy can improve conductivity by up to 50%.
However, manufacturing such advanced designs is not without challenges. Precision in extrusion processes is essential. Minor flaws in the design can lead to poor thermal performance. Additionally, the balance between weight and strength remains a concern. Manufacturers must constantly innovate while addressing these issues to meet evolving market demands.
Top 10 Aluminium Extrusion Heat Sink Designs for Optimal Cooling Solutions
This chart illustrates the cooling efficiency of the top 10 innovative aluminium extrusion heat sink designs, measured in Watts per Kelvin (W/K). These designs have been evaluated for their thermal performance to optimize cooling solutions in various applications.
Applications of Aluminium Extrusion Heat Sinks in Various Industries
Aluminium extrusion heat sinks are critical across many industries. They offer effective thermal management solutions for electronic devices, automotive components, and industrial machinery. With the increasing demand for efficient cooling systems, the market for aluminium-based heat sinks continues to grow. According to a recent report, the global market size for heat sinks is expected to reach $5 billion by 2026.
In the electronics industry, these heat sinks dissipate heat in devices such as computers and LED lights. They ensure longevity and performance by maintaining optimal temperatures. Similarly, in the automotive sector, aluminium heat sinks contribute to the efficiency of electric vehicles by cooling batteries and power electronic systems. This application can enhance vehicle safety and performance.
Tip: When designing heat sinks, consider airflow direction. Proper alignment can greatly boost cooling efficiency.
However, not all designs are flawless. Some may underperform due to inadequate surface area or airflow disruption. It's essential to evaluate each application carefully to avoid costly mistakes. In industrial settings, precision in design can significantly affect cooling performance and energy consumption.
Tip: Invest time in prototyping. Testing various designs can reveal which works best for specific applications.
Evaluating Performance Metrics for Heat Sink Efficiency
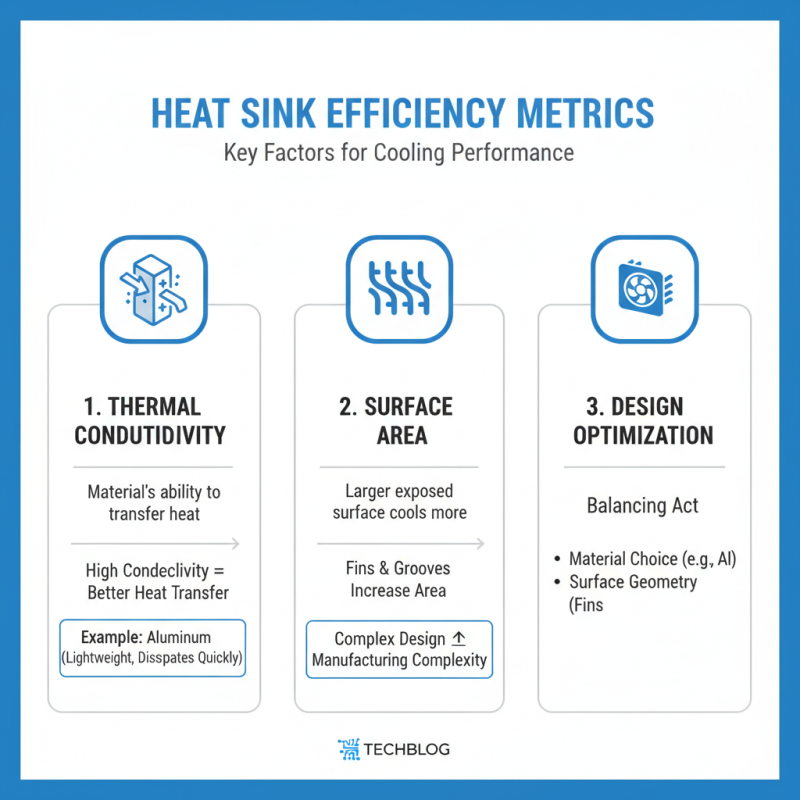
When evaluating heat sink efficiency, several performance metrics matter. Thermal conductivity is crucial. High conductivity materials transfer heat effectively. Aluminum is often favored; it dissipates heat quickly and is lightweight. Surface area plays a vital role too. Designs with larger surfaces cool better. Fins and grooves increase this area significantly but can complicate manufacturing.
Another metric is airflow. Enhanced airflow around the heat sink improves heat dissipation. Fans or natural convection can help here. Efficiency drops if airflow is obstructed. Some designs have intricate shapes to direct airflow better. However, they are harder to produce and can be cost-prohibitive.
Real-world applications vary greatly. In some cases, the heat sink may perform below expectations. This can arise from poor design decisions or material choices. Designers should test prototypes thoroughly. Scaling up a successful design is not always straightforward. What works on paper might not hold up in practice. Adjusting designs constantly is necessary for optimal results.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Aluminium Door China Options for Your Home?
-
What is Aluminium Surface Treatment Methods and Their Benefits?
-

2026 Top Aluminium Profile For Doors And Windows Trends to Watch?
-

2026 How to Optimize the Aluminium Process for Maximum Efficiency?
-
How to Choose the Right Aluminium Extrusion Grades for Your Project?
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing Aluminium Extrusions in NZ